
Demystifying Data, Information and Insight
In this article, we are going to see how to try and get an intuitive understanding of the differences that define Data, Information and insight. While the distinction may seem apparent, in practice there is no clear line between what constitutes information and data. This article will delve into practical examples and scenarios to illustrate these concepts, helping you to not only distinguish between them but also to understand how to transform one into the other in a business setting. Ultimately, grasping these distinctions and their interplay is essential for harnessing the true power of data in driving informed and strategic actions within any organization.
Moreover, what we are aiming to do in this series of articles is to create a very punchy, quick “self-help” guide to anyone new or even somewhat familiar to extracting insight from data. If however, you want to dive deeper, we also have much more technical articles (e.g. discussing the intersection of AI and Big-Data analytics or setting up data mining teams) that will be coming soon on the Neuralgap website https://neuralgap.io/
Data vs. Information vs. Insight
Think of data as the foundational elements in its most unrefined form. Information emerges when these elements are processed and contextualized. The transition from data to information involves a series of steps that enhance the usability and relevance of the original material. Let’s make these attributes a little clearer with some segmentations and examples below:
Markers of Data
Think of data as akin to the raw ingredients in a recipe – essential but not yet transformed into a finished dish. This unprocessed state of data is both its strength and limitation. It offers a direct, unfiltered view of the underlying facts, yet its disorganized nature often requires further processing to unlock its potential. The diversity of data, encompassing both quantitative numbers and qualitative observations, provides a rich tapestry of source material. However, its immediate utility is limited, demanding insightful analysis to transform these disparate data points into coherent and actionable information.
Raw Data
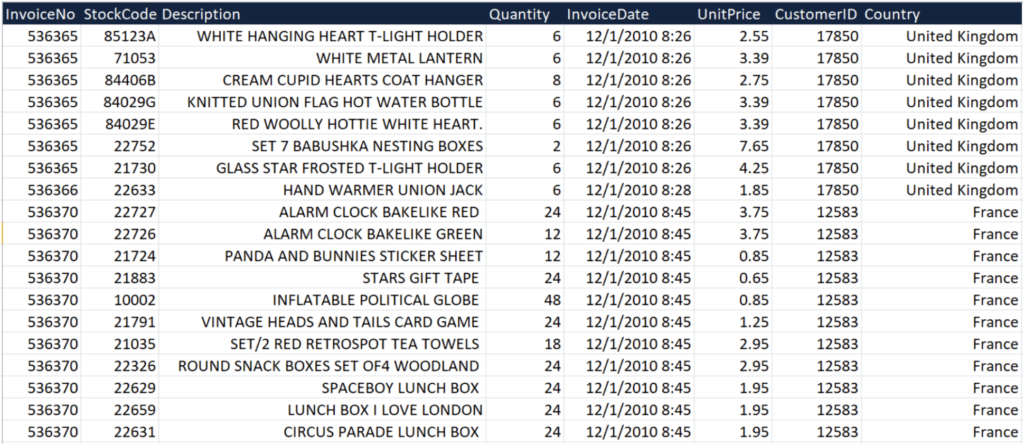
Information
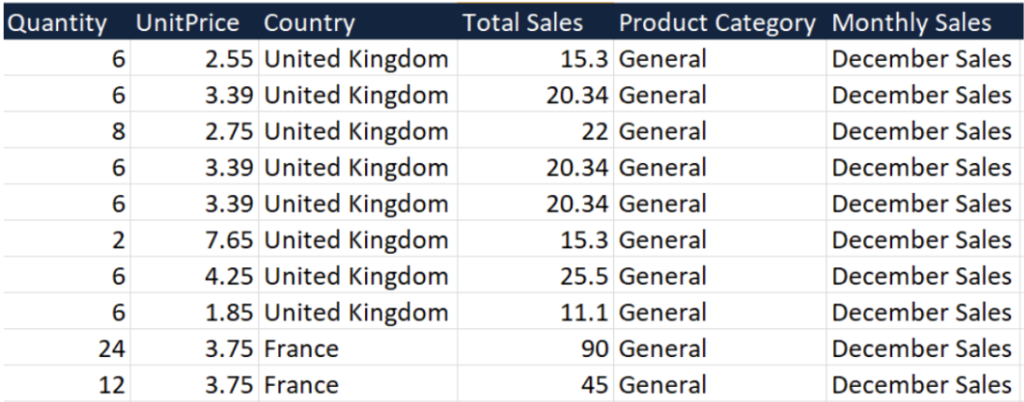
Insight

What is Actionable Information?
This is one of the most valuable assets of a business. Actionable insights stands apart as the kind of information that not only informs but also empowers and guides actions. For example, the above insight actually can cause action (albeit even if it is to refine the information gathering process further). To be truly actionable, information must possess certain qualities that elevate it beyond mere data or basic insights.
Markers of Actionable Information
Actionable information is characterized by its precision and relevance to specific tasks or decisions. It's not just about being accurate; it's about being pertinent to the context at hand. This specificity ensures that the information directly impacts the decision-making process. And its a lot harder than we think - according to a survey by Forrester, while 74% of firms say they want to be “data-driven,” only 29% maintain that they are good at connecting analytics to action. This insight-to-execution process is the final part of creating a feedback loop that enables data to ultimately drive action. Characteristics that make up actionable insights can be characterized by:
- Specific and Relevant: Actionable information is specific and directly relevant to the task or decision at hand.
- Timely: It is available at the right time to influence decisions or actions.
- Clear and Understandable: Information must be clear and easily understood to be actionable.
- Credible and Reliable: Actionable information is based on credible, reliable sources.
- Leads to a Clear Course of Action: It suggests or leads to a clear course of action or decision.
Markers of Tar-Pit “Information”
Conversely, certain types of information can act as traps, hindering decision-making processes. This "Tar-Pit" information is characterized by several detrimental qualities.
- Overwhelming Quantity: Too much information can lead to analysis paralysis.
- Irrelevance or Misleading: Information that is irrelevant or misleading hinders decision-making.
- Lack of Timeliness: Information that is not timely may become obsolete or useless.
- Complexity and Ambiguity: Excessively complex or ambiguous information can be difficult to act upon.
- Lack of Reliability: Information lacking in credibility or reliability can lead to poor decisions.
Interested in knowing more? Schedule a Call with us!
At Neuralgap - we deal daily with the challenges and difficulties in implementing, running and mining data for insight. Neuralgap is focussed on enabling transformative AI-assisted Data Analytics mining to enable ramp-up/ramp-down mining insights to cater to the data ingestion requirements of our clients.
Our flagship product, Forager, is an intelligent big data analytics platform that democratizes the analysis of corporate big data, enabling users of any experience level to unearth actionable insights from large datasets. Equipped with an intelligent UI that takes cues from mind maps and decision trees, Forager facilitates a seamless interaction between the user and the machine, employing the advanced capabilities of modern LLMs with that of very highly optimized mining modules. This allows for not only the interpretation of complex data queries but also the anticipation of analytical needs, evolving iteratively with each user interaction.
If you are interested in seeing how you could use Neuralgap Forager, or even for a custom project related to very high-end AI and Analytics deployment, visit us at https://neuralgap.io/
